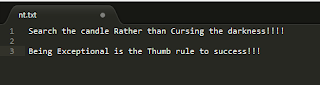
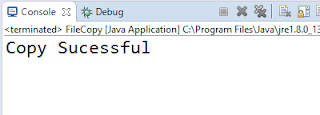
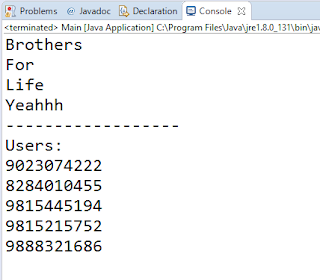
Following Code will help you to copy contents from one file to another with or without appending.
Code:
import java.io.*;
public class FileCopy {
void copy(File s,File d,boolean a){
FileReader r=null;
BufferedReader br=null;
FileWriter w=null;
BufferedWriter bw=null;
try {
r=new FileReader(s);
br=new BufferedReader(r);
w=new FileWriter(d,a);
bw=new BufferedWriter(w);
String l;
while((l=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write("\n"+l);
}bw.newLine();
System.out.println("Copy Sucessful");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error: "+e);
//e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
try {
r.close();
br.close();
bw.close();
w.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
System.out.println("Error: "+e2);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] nt) {
FileCopy fRef=new FileCopy();
File src=new File("C:/Users/mrdis/Downloads/nt.txt");
File des=new File("C:/Users/mrdis/Downloads/nti.txt");
boolean append=true;
fRef.copy(src, des, append);
}
}
Code:
import java.io.*;
public class FileCopy {
void copy(File s,File d,boolean a){
FileReader r=null;
BufferedReader br=null;
FileWriter w=null;
BufferedWriter bw=null;
try {
r=new FileReader(s);
br=new BufferedReader(r);
w=new FileWriter(d,a);
bw=new BufferedWriter(w);
String l;
while((l=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write("\n"+l);
}bw.newLine();
System.out.println("Copy Sucessful");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error: "+e);
//e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
try {
r.close();
br.close();
bw.close();
w.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
System.out.println("Error: "+e2);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] nt) {
FileCopy fRef=new FileCopy();
File src=new File("C:/Users/mrdis/Downloads/nt.txt");
File des=new File("C:/Users/mrdis/Downloads/nti.txt");
boolean append=true;
fRef.copy(src, des, append);
}
}