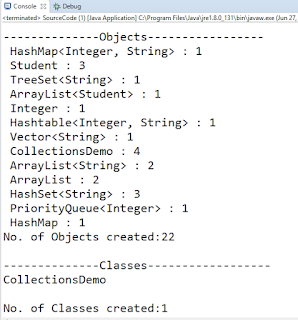
Following code will print the number and names of Objects,Classes,Interfaces created in java source file.
Code:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class SourceCode {
public static void main(String[] nt){
File src=null;
FileReader fin=null;
BufferedReader br=null;
int o=0,c=0,i=0;
try {
Date d=new Date();
long start=d.getTime();
src=new File("F:/Session14/src/com/auribises","CollectionsDemo.java");
fin=new FileReader(src);
br=new BufferedReader(fin);
String line="";
HashMap<String,Integer> mp=new HashMap<String,Integer>();
StringBuffer data=new StringBuffer();
StringBuffer datai=new StringBuffer();
while((line=br.readLine())!=null) {
if(line.contains("new")){
o++;
int k=line.indexOf("new");
int l=line.indexOf("(",k+3);
if(mp.containsKey(line.substring(k+3,l))){
int x=mp.get(line.substring(k+3,l));
mp.put(line.substring(k+3,l),++x);
}
else{
mp.put(line.substring(k+3,l),1);
}
}
if(line.contains("class")){
c++;
int k=line.indexOf("class");
int l=line.indexOf("{",k+6);
data.append(line.substring(k+6,l)+"\n");
}
if(line.contains("interface")){
i++;
int k=line.indexOf("interface");
int l=line.indexOf("{",k+10);
datai.append(line.substring(k+10,l)+"\n");
}
}
System.out.println(src.getName());
System.out.println("\n--------------Objects-----------------");
Set<String> k=mp.keySet();
Iterator<String> it=k.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String x=it.next();
int value=mp.get(x);
System.out.println(x+" : "+value);
}
System.out.println("No. of Objects created:"+o);
System.out.println("\n--------------Classes------------------");
System.out.println(data);
System.out.println("No. of Classes created:"+c);
System.out.println("\n--------------Interfaces---------------");
System.out.println(datai);
System.out.println("No. of Interfaces created:"+i+"\n");
d=new Date();
long stop=d.getTime();
System.out.println("Time Taken:"+(stop-start)+" miliseconds");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Some Error"+e);
}finally {
try {
fin.close();
br.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
System.out.println("Error:"+e2);
}
}
}
}
Code:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class SourceCode {
public static void main(String[] nt){
File src=null;
FileReader fin=null;
BufferedReader br=null;
int o=0,c=0,i=0;
try {
Date d=new Date();
long start=d.getTime();
src=new File("F:/Session14/src/com/auribises","CollectionsDemo.java");
fin=new FileReader(src);
br=new BufferedReader(fin);
String line="";
HashMap<String,Integer> mp=new HashMap<String,Integer>();
StringBuffer data=new StringBuffer();
StringBuffer datai=new StringBuffer();
while((line=br.readLine())!=null) {
if(line.contains("new")){
o++;
int k=line.indexOf("new");
int l=line.indexOf("(",k+3);
if(mp.containsKey(line.substring(k+3,l))){
int x=mp.get(line.substring(k+3,l));
mp.put(line.substring(k+3,l),++x);
}
else{
mp.put(line.substring(k+3,l),1);
}
}
if(line.contains("class")){
c++;
int k=line.indexOf("class");
int l=line.indexOf("{",k+6);
data.append(line.substring(k+6,l)+"\n");
}
if(line.contains("interface")){
i++;
int k=line.indexOf("interface");
int l=line.indexOf("{",k+10);
datai.append(line.substring(k+10,l)+"\n");
}
}
System.out.println(src.getName());
System.out.println("\n--------------Objects-----------------");
Set<String> k=mp.keySet();
Iterator<String> it=k.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String x=it.next();
int value=mp.get(x);
System.out.println(x+" : "+value);
}
System.out.println("No. of Objects created:"+o);
System.out.println("\n--------------Classes------------------");
System.out.println(data);
System.out.println("No. of Classes created:"+c);
System.out.println("\n--------------Interfaces---------------");
System.out.println(datai);
System.out.println("No. of Interfaces created:"+i+"\n");
d=new Date();
long stop=d.getTime();
System.out.println("Time Taken:"+(stop-start)+" miliseconds");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Some Error"+e);
}finally {
try {
fin.close();
br.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
System.out.println("Error:"+e2);
}
}
}
}
Output: