The Standard Deviation is a measure of how spread out numbers are.
Its symbol is σ (the greek letter sigma)
Following Code will calculate the Standard Deviation:
Code::
import mathdef average(l): #function to calculate average(mean)
total=0.0
for i in l:
total=total+int(i)
if(len(l)==0): return 0
else: return(total/len(l))
def standardeviation(l,ave): #function to calculate standard deviation
diff=0.0
for i in l:
x=int(i)-ave
diff=diff+x*x
if(len(l)==0): return 0
else :return(math.sqrt(diff/len(l)))
lst=[]
num=input("Enter Values ,enter -1 to end:")
while num!='-1':
lst.append(num)
num=input()
ave=average(lst)
print("Average is:",ave)
sd=standardeviation(lst, ave)
print("Standard Deviation :",sd)
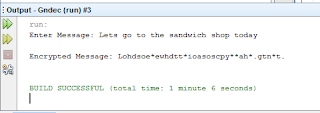
Output::