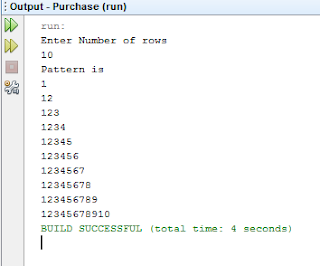
Following program accepts no of rows and print a triangle pattern as given below:
import java.util.*;
public class Inches
{
public static void main(String[] nt)
{
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Number of rows");
int x=in.nextInt();
System.out.println("Pattern is");
for(int i=1;i<=x;i++)
{ for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
System.out.print(j);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:
Test Data
Input number of rows :5
Input number of rows :5
Output :
1
12
123
1234
12345
public class Inches
{
public static void main(String[] nt)
{
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Number of rows");
int x=in.nextInt();
System.out.println("Pattern is");
for(int i=1;i<=x;i++)
{ for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
System.out.print(j);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output: